Discover the Fascinating Truth: Do Blue Jays Migrate?
Yes, blue jays migrate. Blue jays are highly recognizable birds known for their striking blue feathers and tufted crests that are prominent on their heads.
They are also admired for their intelligence and adaptability. However, their migration habits may not be as well-known. Like many bird species, blue jays do migrate, but with some variation depending on their geographic location. Some blue jays in the northern part of their range may migrate southward during the colder winter months, while others in southern regions may be year-round residents.
Migratory behavior is often driven by factors like food availability, climate and competition for resources. To better understand the migration of these magnificent birds, it is important to examine the factors that influence their movements and patterns.
Blue Jays Habitat Range And Distribution
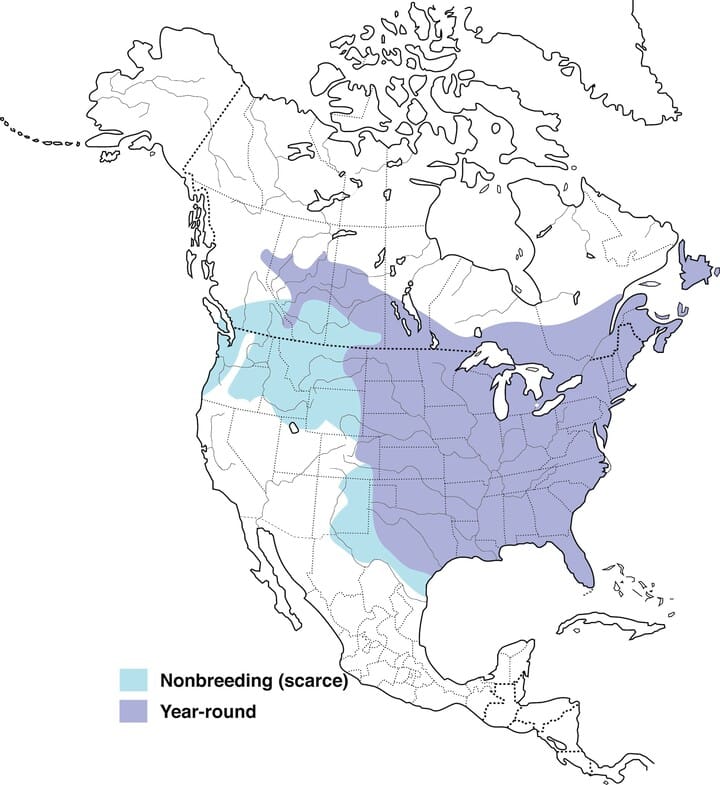
Blue jays are one of the most widespread and easily identified bird species in north america. These beautiful birds are known for their striking blue feathers, intelligent behavior, and distinctive call. One of the most common questions people have about blue jays is whether they migrate or not.
In this section, we will explore the blue jays’ habitat range and distribution, as well as the factors that affect their habitat and migration patterns.
Where Blue Jays Are Found And Their Preferred Habitat
Blue jays are found throughout north america, from canada to texas, and from the east coast to the west coast. These birds can thrive in a variety of habitats, including forests, woodlands, parks, and residential areas. However, blue jays tend to prefer deciduous and mixed forests, as they provide a rich source of acorns, nuts, and fruits that they feed on.
Blue jays are highly adaptable and can be found in urban areas as well. They can often be seen perched on trees in residential neighborhoods or visiting bird feeders in suburban gardens. Blue jays are also known to migrate to warmer regions during winter, making their way to the southern parts of the united states and mexico.
Factors Affecting Blue Jays’ Habitat And Migration Patterns
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the blue jays’ habitat range, distribution, and migratory patterns. These include:
- Food availability: Blue jays feed on a variety of food types, including acorns, nuts, insects, and fruits. The availability of these food sources can influence their habitat selection and migratory patterns.
- Climate and weather conditions: Blue jays are sensitive to climate and weather changes, and they may adjust their migration patterns to adapt to these conditions. Warmer temperatures and milder winters may alter their migration routes or cause them to remain in their preferred habitat for longer periods.
- Habitat destruction: The loss of forested areas and habitat destruction due to human activities can have a significant impact on blue jays’ breeding and migratory patterns.
- Predator and prey dynamics: Blue jays are preyed upon by various bird species and animals, which may affect their behavior and distribution. High predator populations or low prey density can lead to changes in their migratory patterns or habitat selection.
Blue jays are widespread birds that can thrive in a variety of habitats and environments. Their preferred habitat is deciduous and mixed forests, which provide them with ample food sources. Several factors, including food availability, climate conditions, habitat destruction, predator and prey dynamics, can affect their habitat range and migration patterns.
Understanding The Factors That Influence Bird Migration
Do Blue Jays Migrate?
Blue jays are one of the most common birds in north america. Many people wonder if they migrate or not. The short answer to the question is yes, blue jays do migrate! Bird migration is a natural phenomenon that happens across the world.
In this section, we will delve deeper into blue jays’ migration patterns and the underlying factors that influence them.
The Internal Biological Clock And Its Role In Bird Migration
The internal biological clock, also known as circadian rhythm, helps birds to know when it’s time to migrate. The timing of a bird’s migration is important because it ensures they arrive at their destination at the right time. Below are some key points to consider regarding the internal biological clock and bird migration:
- The internal biological clock is responsible for regulating many physiological functions in birds, including sleep patterns, hormone production, and metabolism.
- The biological clock also helps birds navigate by using the position of the sun and stars to determine the time of day and their location.
- Birds have a special protein in their eyes that allows them to sense the earth’s magnetic field. This protein is believed to help birds navigate during migration.
Weather Patterns’ Impact On Bird Migration Patterns
Weather is another significant factor that influences bird migration patterns. Birds are very sensitive to changes in weather, and they use the weather to plan their migration. Here are some key points about how weather affects bird migration:
- Birds use prevailing winds to help them travel long distances during migration. Tailwinds can help birds conserve energy, while headwinds can slow them down and make migration more difficult.
- Birds may delay migration or change course if weather conditions are unfavorable, such as during storms or heavy rain.
- Temperature changes can affect the timing of migration. During warmer winters, some birds may decide to migrate later than usual or not at all.
The Impact Of Seasonal Changes On Bird Migration
Seasonal changes also play a significant role in bird migration. Changes in food availability, daylight hours, and temperature all impact birds’ migratory patterns. Here are some important points to note about how seasonal changes affect bird migration:
- Birds migrate to breeding grounds where they can raise their young in ideal conditions. During the breeding season, birds require more food, so they migrate to areas where food is abundant.
- The length of daylight hours changes with the seasons, which helps to trigger migration patterns in birds.
- Changes in temperature, especially during the fall, trigger birds to migrate south in search of warmer temperatures.
Understanding the factors that influence bird migration is essential for appreciating how and why birds migrate. Birds use a combination of internal and external cues to plan their migration. We hope this section has imparted valuable insights into blue jays’ migration patterns and the role weather patterns and seasonal changes play in them.
The Migration Pattern Of Blue Jays
Do Blue Jays Migrate: The Migration Pattern Of Blue Jays
Blue jays are brightly colored birds that belong to the corvidae family. They are known for their striking blue, black, and white plumage and their raucous calls. Many people wonder whether blue jays migrate, given that some bird species do, and it is a fascinating subject to explore.
Examination Of Blue Jays’ Migration Patterns
Blue jays are migratory birds and move from their summer breeding grounds to warmer regions during the winter season. They are known to migrate southwards from canada during the fall season and can travel up to a distance of 2500 kilometers.
During the winter season, blue jays can be found in the southern united states, with some venturing further south to central america.
Comparing Blue Jays’ Migration Pattern To Other Bird Species
Blue jays are one of the few bird species that take a slightly different migration path every year. Unlike other birds that follow a fixed route, blue jays tend to move in a more scattered fashion, adapting their path as per the availability of food and weather conditions.
Blue jays are also known to fly solo during their migration journey, unlike the cooperative migration pattern of some other bird species like geese and ducks.
Identifying The Factors That Make Blue Jays’ Migration Unique
There are various factors that make blue jays’ migration unique. Some of these include:
- Food availability: Blue jays tend to migrate towards areas where there is easily accessible food. During the winter season, they often feed on acorns, nuts, and seeds, which can be found in the southern united states.
- Adaptation to weather conditions: Blue jays are known to move towards areas with mild weather conditions, particularly during winters. If the temperature drops too low in their current location, blue jays will migrate to a warmer region to keep themselves comfortable.
- Independent migration: Unlike other bird species, blue jays tend to migrate alone and do not follow a fixed migration path. This means that they have the freedom to choose their route, which can lead to more variety in population distribution and growth.
Blue jays are migratory birds that undertake a complex and unique migration pattern. They tend to move towards areas where food is readily available and adapt to weather conditions as required. Their independent migration patterns make them stand out among other bird species and provide a fascinating subject of study.
The Significance Of Blue Jays Migration
Blue jays are known for their stunning blue feathers and striking black collar. But did you know that these beautiful birds also have a migration pattern? In this blog post, we’ll explore the significance of blue jays’ migration and why it’s important to protect it.
Let’s dive in!
The Ecological Importance Of Blue Jays’ Migration
Blue jays may be captivating to look at, but they’re also an essential part of our ecosystem. Here are some key ecological benefits of blue jays’ migration:
- Seed dispersal: Blue jays are seed dispersers. They eat fruits and nuts and then disperse the seeds as they travel. This helps in the regeneration of forests and the growth of new trees and plants.
- Natural pest control: Blue jays also help to control the population of insects and invertebrates. By consuming these pests, blue jays serve as an important natural pest control system.
- Diversity of species: The migration of blue jays plays a crucial role in maintaining the diversity of species. As they move from one habitat to the other, they help spread genetic diversity and maintain healthy ecosystems.
The Economic And Cultural Impact Of Blue Jays’ Migration
The migration of blue jays also has significant economic and cultural impacts. Here are some key points:
- Tourism: Blue jays are a popular bird species to watch among birders and nature enthusiasts. The migration of blue jays in the fall attracts thousands of tourists every year. This activity boosts local economies and supports jobs related to tourism.
- Traditional native american culture: Blue jays hold a significant place in the traditional cultures of native american communities. They are viewed as sacred birds and symbolize clarity, activity, and vibrancy. The migration of blue jays is often celebrated through traditional dances and ceremonies.
- Agricultural impact: Blue jays play a role in the agriculture industry as well. They help to disperse the seeds of crops and control the population of pests. The migration patterns of blue jays can impact the timing of planting and harvesting crops.
The Conservation Efforts Aimed At Protecting Blue Jays’ Migration Pattern
The migration of blue jays is vital for the health of ecosystems, economies, and culture. That’s why it’s essential to protect their migration pattern. Here are some conservation efforts currently in place:
- Habitat protection: The protection of blue jays’ habitat is crucial for their survival. Conservation organizations are working to protect forests and other habitats where blue jays thrive.
- Monitoring migration: Scientists are monitoring blue jays’ migration patterns to understand how they may be impacted by climate change and habitat loss. This information helps them to protect this bird species effectively.
- Public education: Educating the public about blue jays’ migration and their ecological and cultural importance is also crucial for their protection. Through awareness campaigns, people can understand the significance of blue jays’ migration and work towards their conservation.
The migration of blue jays is much more than a beautiful sight to behold. It’s a critical process that impacts our ecosystems, economies, and cultures. By protecting their migration pattern, we can ensure that blue jays thrive for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions For Do Blue Jays Migrate
Do Blue Jays Migrate In The Winter?
Yes, blue jays do migrate in the winter when their natural food sources become scarce. They move in flocks to areas with more abundant food sources. Blue jays from northern regions migrate southward, while those from southern regions move to the warmer tropics.
Where Do Blue Jays Migrate To?
Blue jays migrate to different locations depending on their region of origin. Those from the northern regions migrate to southern regions, while those from southern regions migrate to the tropics. They typically travel in large flocks along established paths or flyways.
When Do Blue Jays Migrate?
Blue jays typically begin their migration during the fall months, between september and november. The exact timing may vary depending on the location and climate. They start returning to their original breeding areas in the spring, usually around march or april.
How Far Do Blue Jays Migrate?
The distance blue jays migrate varies depending on their location, but they can travel up to several thousand kilometers. Some blue jays from canada and the northern united states will fly as far south as mexico and central america to avoid harsh winter conditions.
How Do Blue Jays Navigate During Migration?
Blue jays have a strong internal compass that helps them navigate during migration. They are also able to detect the earth’s magnetic field and use the position of the sun to guide their travels. Additionally, they can recognize visual landmarks and use these to help orient themselves.
Conclusion
It’s clear that blue jays are one of the most beautiful birds out there. But, whether they migrate or not is still a subject of discussion. Some studies suggest that blue jays are erratic migrators, and their behavior varies depending on the location they’re in.
Some blue jays only migrate when there’s a scarcity of food or when they’re experiencing harsh weather conditions. While others migrate twice a year, splitting their time between both southern and northern regions of america. The decision to migrate seems to depend on the bird’s age, sex, and geographical location, making it a little tricky to generalize.
However, one thing is certain; if you’re a bird-watcher, you won’t miss the chance to witness the beauty of the blue jays, migratory or not. So next time you hear their distinctive calls, pay close attention, and who knows? You might just observe a migration in action.